Incremental Analysis: Definition, Types, Importance, and Example

Incremental costing helps assess the effectiveness of these campaigns. They need to compare the additional costs (advertising, discounts, and https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ staff overtime) against the incremental benefits (increased footfall, sales, and brand visibility). In summary, while incremental costing provides valuable insights, decision-makers must recognize its limitations. Combining it with other decision tools and considering a holistic view ensures better-informed choices. Remember, every decision involves trade-offs, and understanding these limitations enhances our decision-making process.
Importance of Incremental Cost
By analyzing these incremental costs, the firm can allocate its resources effectively and maximize returns. As a result, the total incremental cost to produce the additional 2,000 units is $30,000 or ($330,000 - $300,000). The negative $25,000 incremental cost signals that outsourcing would reduce production costs by $25,000 for this volume. incremental cost For instance, evaluating expanding monthly production from 10,000 units to 15,000 units means the incremental change is 5,000 units. Also called marginal analysis, the relevant cost approach, or differential analysis, incremental analysis disregards any sunk cost (past cost).
Understanding Incremental Costs
- Be sure to read until the end for answers to frequently asked questions.
- Incremental costs help to determine the profit maximization point for a company or when marginal costs equal marginal revenues.
- Whether it's a small operational decision or a major strategic move, incremental analysis helps navigate the complexities of business with clarity and precision.
- In essence, it assists a company in making profitable business decisions.
- Companies look to analyze the incremental costs of production to maximize production levels and profitability.
- By considering incremental cost, businesses can gain valuable insights into the true cost of producing additional units or implementing new projects.
But the incremental benefit—customer retention and word-of-mouth marketing—far outweighs this cost. From an economic perspective, incremental cost embodies opportunity cost—the value of the next best alternative foregone. Imagine a bakery deciding whether to produce an extra batch of croissants. The incremental cost includes not only the flour, butter, and labor but also the potential revenue lost by not using the same resources elsewhere (e.g., making baguettes). Always consider the relevant factors, time horizon, and assumptions when applying it to real-world scenarios. By incorporating incremental cost into decision-making, we can optimize resource allocation and achieve better outcomes.
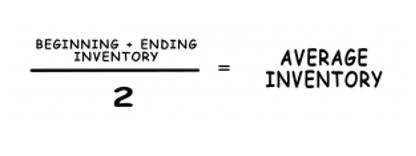
What Is Incremental Cost?
This allows individuals and organizations to assess the value and feasibility of each option before making a final choice. In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of comparing benefits and costs, providing insights from various perspectives. Incremental cost is the cost incurred due to an additional unit of a product being produced. This is the increase/decrease in the cost of producing one more additional unit or serving one more additional customer.
Incremental Cost Decisions
- Continuing the example, let’s say it costs $100,000 to produce the 10,000 units in a typical month.
- By considering the additional costs incurred and the potential benefits gained, individuals and businesses can make informed choices that align with their objectives.
- Incremental costs are also used in the management decision to make or buy a product.
- Fixed costs are those that do not change with production or sales, such as rent and insurance.
- Remember, every decision involves trade-offs, and understanding these limitations enhances our decision-making process.
- When analyzing different options, businesses should focus on incremental costs rather than sunk costs to make rational and forward-looking decisions.
- However, none of it will include the fixed costs since they will not change due to volume fluctuation.
As technology advances, AI algorithms optimize incremental decisions. They analyze vast datasets, predict outcomes, and recommend cost-effective paths. Imagine an e-commerce platform adjusting ad spending based on incremental conversion rates. The future lies in harnessing AI's power for precision decision-making. Continuing the example, let’s say it costs $100,000 to produce the 10,000 units in a typical month. For example, if you normally produce 10,000 units of a product per month, this base monthly volume is 10,000 units.

The management must look at the additional cost of producing the products under one roof. This could mean more deliveries from vendors or even more training costs for employees. An incremental cost is the difference in total costs as the result of a change in some activity.

Incremental Cost
Suppose a hospital is considering offering a new specialized treatment. Incremental costing helps evaluate the impact on patient care and financial sustainability. They need to weigh the additional costs (specialized equipment, staff training, and patient care) against the incremental benefits (better patient outcomes, reputation, and potential referrals). Incremental costs are also evaluated in overall business strategies. https://www.bookstime.com/articles/cash-flow-from-financing-activities For instance, a company merger might reduce overall costs of because only one group of management is required to run the company. Producing the products, however, might bring incremental costs because of the downsizing.

































